以这样种方式添加源,总会出现warning
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:dawidd0811/neofetch
Warning: apt-key is deprecated. Manage keyring files in trusted.gpg.d instead (see apt-key(8)).
gpg: 找不到有效的 OpenPGP 数据。
参考别人的文章:https://suay.site/?p=526
原文如下:
The apt-key command manages keys that are responsible for verifying the signature of application package repositories.
Now, whenever you use the apt-key command, you will receive the message:
|
1 |
Warning: apt-key is deprecated. Manage keyring files in trusted.gpg.d instead (see apt-key(8)).
|
It means that the apt-key program is now deprecated. Now we should use trusted.gpg.d to manage keyfiles. Translated into human language, now we have to add files ourselves to the /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ folder.
This method will use the /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ directory to store the public GPG key ring files. It has been available since early 2017.
If you look at the recommended man page (man apt-key), it says that this command and all its functions are deprecated.
There are two options for how you can proceed in this situation.
You can continue to use apt-key
Despite the assurances in the documentation, the apt-key program works as usual and performs all its functions.
At the same time, the apt-key command will not be removed for quite a long time, at least several years. It may not be removed at all for compatibility.
Therefore, basically, you can ignore the warning “apt-key is deprecated”.
How to add keys in a new way
The new “modern” version is poorly documented, let's try to fill this gap.
Now the keys need to be added with the following commands.
If a remote key file is added:
|
1 |
curl -s URL | sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/NAME.gpg --import
|
If a local key file is added:
|
1 |
cat URL.pub | sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/NAME.gpg --import
|
In these commands, you need to substitute:
- URL - address of the .pub file
- NAME - you can choose any file name
- FILE - filename of the .pub file
Then be sure to run the following command to set the correct file permissions:
|
1 |
sudo chmod 644 /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/NAME.gpg
|
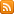
Example. If you already know the URL of the required public key, use wget or curl to download and import it. Remember to update the file permissions from 600 to 644.
|
1
2 |
curl -s https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/earth.gpg --import
sudo chmod 644 /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/earth.gpg
|
Alternatively, you can get the key from the keyserver:
|
1
2 |
sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/rabbit.gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv 6B73A36E6026DFCA
sudo chmod 644 /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/rabbit.gpg
|
How to view information about installed keys
To view information about the installed key, run a command of the form:
|
1 |
gpg --list-keys --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/FILE.gpg
|
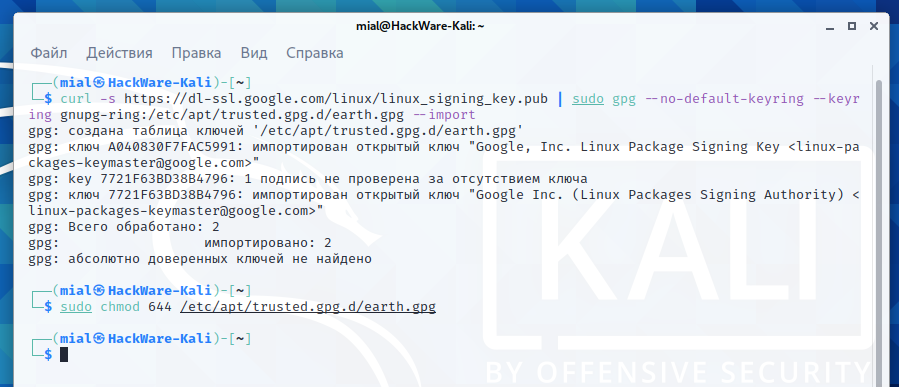
For instance:
|
1 |
gpg --list-keys --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/earth.gpg
|
As said, the old command also works:
How to remove a key added by a new method
If you need a command analogue:
|
1 |
sudo apt-key del 7D8D08F6
|
Now, to remove the key, simply delete the file with commands like:
|
1
2 |
cd /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/
sudo rm NAME.gpg
|
But “apt-key del” also works.
How to remove a key added with apt-key add
If you want to delete individual keys, then use a command like this:
To find out the KEY_ID, run the command
find the key you want, for example:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6 |
/etc/apt/trusted.gpg
--------------------
pub rsa4096 2016-04-12 [SC]
EB4C 1BFD 4F04 2F6D DDCC EC91 7721 F63B D38B 4796
uid [ неизвестно ] Google Inc. (Linux Packages Signing Authority) <linux-packages-keymaster@google.com>
sub rsa4096 2019-07-22 [S] [ годен до: 2022-07-21]
|
Look at the sequence of numbers and letters in the pub field - this is a hash. In this example, we are interested in the line
|
1 |
EB4C 1BFD 4F04 2F6D DDCC EC91 7721 F63B D38B 4796
|
To delete this key, you need to run the command (note that spaces have been removed from the hash):
|
1 |
sudo apt-key del EB4C1BFD4F042F6DDDCCEC917721F63BD38B4796
|
How to remove all keys added with apt-key add
Just delete the /etc/apt/trusted.gpg file:
|
1 |
sudo rm /etc/apt/trusted.gpg
|
|